
It contains the cell bodies of the following cells: It contains the synapses between the synaptic processes of rod and cone cells and the dendrites of the bipolar and Horizontal cells. Nuclei of rods are small, dark, and found at different levels while the cone nuclei are large, pale, and found at one level near the outer limiting membrane. It contains the cell bodies of rod and cone cells. It is formed by the junctional complexes between the photoreceptor cells and the supporting Müller’s cells. T he outer segments of the rod and cones are formed of numerous, flat membranous discs that contain the light-sensitive ”rhodopsin” which initiates the visual impulses. Rods have thin, cylindrical outer segments while cones have short, conical outer segments with their tips invaginated by the microvilli of RPE cells. Rods and cones elongated modified neurons oriented parallel to one another but perpendicular to the retina. There are about 120 million receptor cells in each retina the ratio of rods to cones is 20:1. This layer contains the outer and inner segments of the photoreceptor cells rod and con cells. Layer of rods & cones (The photoreceptors) Renewal of the photoreceptors by phagocytosis of the tips of their outer segments, as indicated by the numerous lysosomes in the apical cytoplasm.Ģ.Restoration of photosensitivity to visual pigments through vitamin A esterification by the abundant smooth endoplasmic reticulum.The RPE together with the structure of retinal continuous capillaries forms the blood-retinal barrier. Isolation of the neural retinal cells from the blood-borne toxic substances: by tight junctions between the adjacent retinal pigmented epithelial cells.Melanin absorbs light after the stimulation of photoreceptors. Absorption of light: as indicated by the presence of numerous melanin granules stored in the apical cytoplasm.The cell base has numerous invaginations and the cell apex, which faces the rods and cones, shows multiple microvilli that surround the tips of the photoreceptors.įunctions of the RPE & its relation to the histological structure: It consists of a single layer of cuboidal cells.
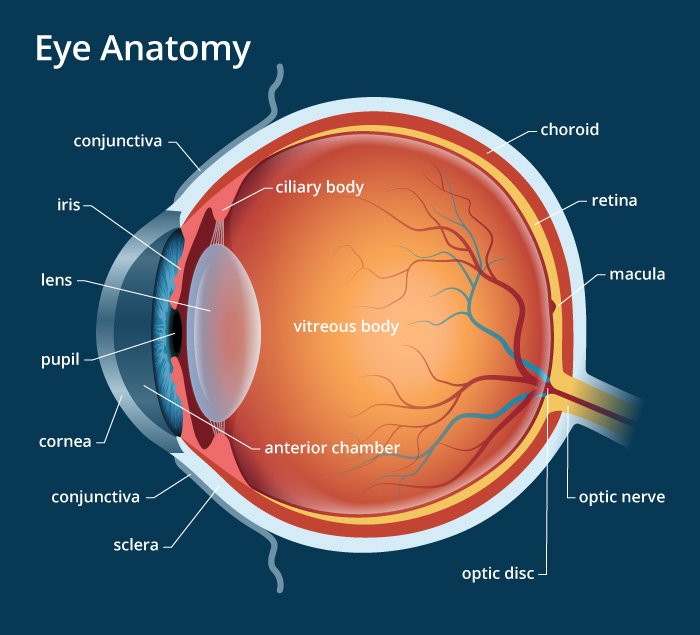
Histologically, the retina is formed of 10 parallel layers, which are from outside inward: 1. Retina proper: an inner photosensitive part.This layer is resting on and firmly attached to the choroid. Pigmented epithelium: an outer non-photosensitive layer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
